Projects
Automated task-free brain mapping for safer epilepsy surgery
RBWH Foundation Grants Round 5
Share this project
Project description
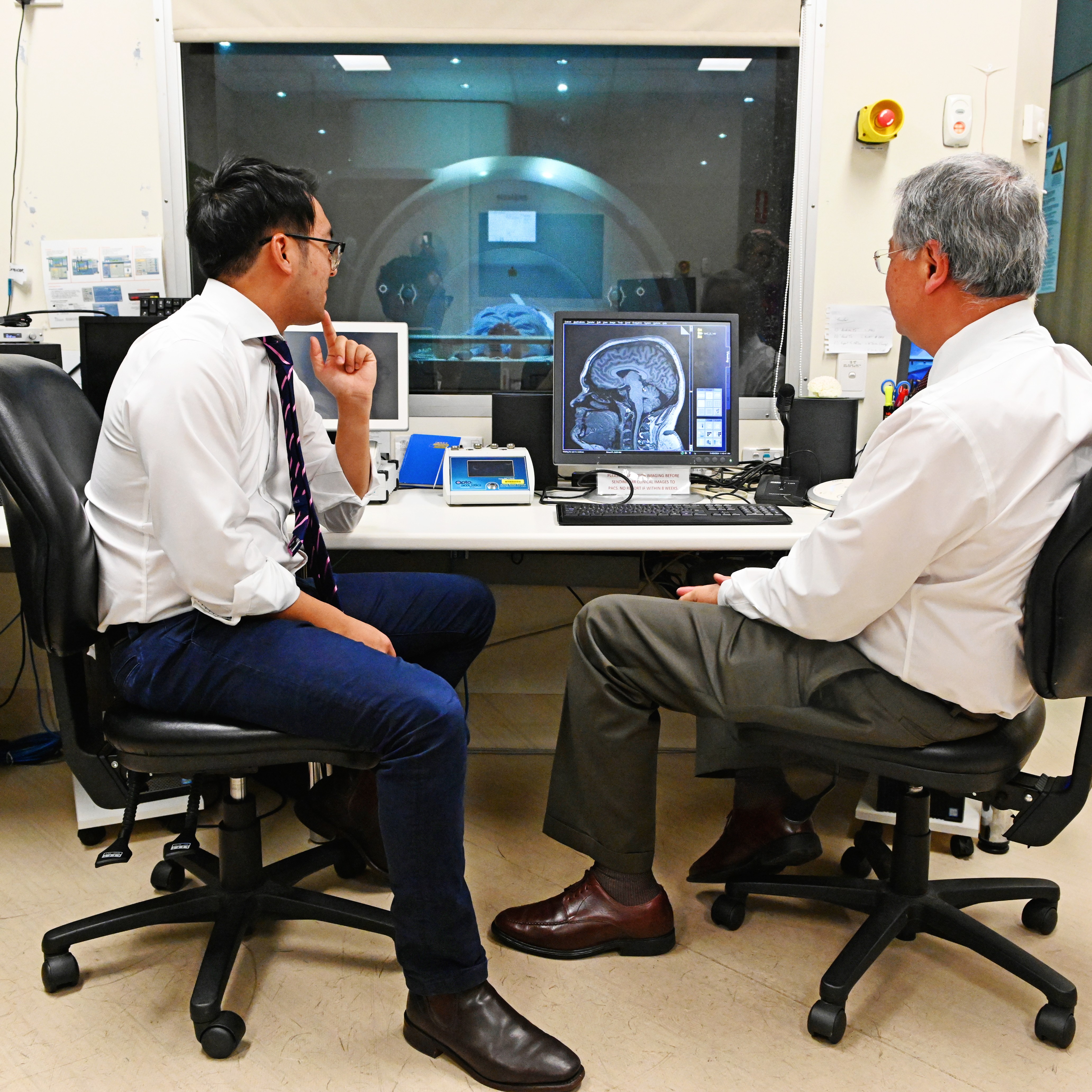
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is routinely used in surgical planning for a number of conditions, including epilepsy.
This project will create and test an automated mapping tool that uses data collected while the patient rests in the scanner, without needing to perform a task.
Why this work is needed
For patients with drug-resistant Temporal Lobe Epilepsy, anterior temporal resection (removal of a section of the brain) can be a life-changing cure. However any brain surgery risks damaging critical brain regions.
To prevent this, surgeons need a precise map of “eloquent” areas that support language and vision. Currently, mapping the brain before surgery requires patients to perform complex tasks inside an MRI scanner, which not all patients are able to do.
There is a critical need to develop new assessment tools that are suitable for all patients.
Expected outcomes
By combining two types of "task-free" scans, one that maps brain activity and one that maps brain wiring, this tool will automatically generate a personalised eloquent “safety” map for each patient.
This will give RBWH surgeons a data-driven tool to plan safer brain operations, helping to preserve vital functions and improve the quality of life for patients with epilepsy.